It’s been a while since my last post about the wonders of modern GPU computing with GLSL but the following concept really took a lot of time to get it to work as intended. Today I’m going to introduce emulated quadruple floating point precision (quad-single-precision) with GLSL. I will use the well-known mandelbrot set to demonstrate the concept.
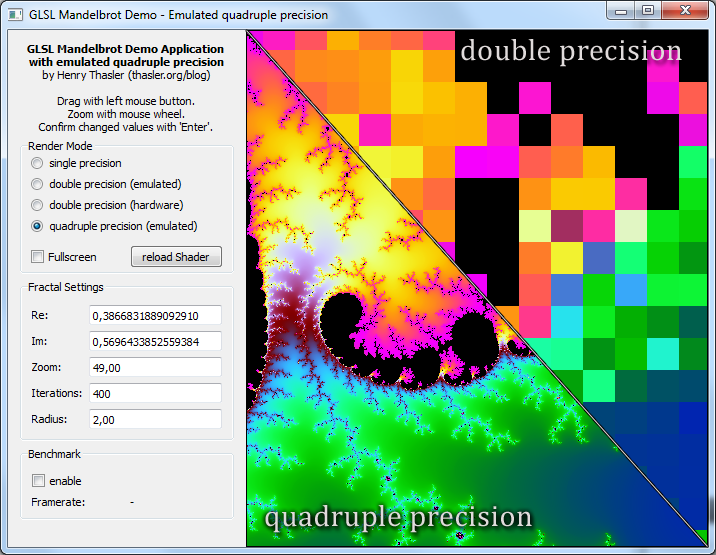
Introduction
The last posts use double precision (hardware and emulated) to calculate mandelbrot sets down to [insert] units per pixel in the complex plane. To push that limit even further I will emulate quadruple precision (quad-precision) using four single precision variables (quad-single). The original concept and the Fortran/C++ sourcecode was developed by Yozo Hi, Xiaoye S. Li and David H. Bailey at Berkeley. It is available as the QD library. I just need to convert and modify this code for GLSL…
The Quad-Single Concept
The concept is basically the same I have described in on of my previous posts about double-single emulation. For quad-precision you just add two more floats to represent your actual value. On the contrary, arithmetic operations are much more difficult to perform, because you must take care of all the carry-over stuff. This results in a lot of difficult and expensive functions to perform just a simple addition. The technical details are described in this paper (PDF).
QT-Application
The Qt application features only minor changes. To improve precision on this end I use long doubles for all variables that eventually end up in the shader.
To make things easier in the shader it gets two vec2 elements instead of four floats with the glUniform2fv-function. That’s why we need a handle for this function:
// define prototype
typedef void (APIENTRYP PFNGLUNIFORM2FVPROC) (GLint location, GLsizei count, const GLfloat *value);
PFNGLUNIFORM2FVPROC glUniform2fv;
// get handle from OpenGL-context
glUniform2fv = (PFNGLUNIFORM2FVPROC) GLFrame->context()->getProcAddress("glUniform2fv");
It is used as follows:
float vec2[2];
vec2[0] = (float)xpos;
vec2[1] = xpos - (double)vec2[0];
glUniform2fv(glGetUniformLocation(ShaderProgram->programId(), "qs_cx"), 2, vec2);
The Shader
I guess the shader has gotten somewhat complex. Nevertheless you can have a look at it and maybe adapt or extend it to your own purpose. The variable names are the same as in the original c++ code. The comments behind the lines are the original code (useful for debugging/comparing).
#version 120
// emulated quadruple precision GLSL library
// created by Henry thasler (thasler.org/blog)
// based on the QD library (http://crd-legacy.lbl.gov/~dhbailey/mpdist/)
uniform int iterations;
uniform float frame;
uniform float radius;
uniform vec2 qs_z;
uniform vec2 qs_w;
uniform vec2 qs_h;
uniform vec2 qs_cx;
uniform vec2 qs_cy;
// inline double quick_two_sum(double a, double b, double &err)
vec2 quick_2sum(float a, float b)
{
float s = a + b; // double s = a + b;
return vec2(s, b-(s-a)); // err = b - (s - a);
}
/* Computes fl(a+b) and err(a+b). */
// inline double two_sum(double a, double b, double &err)
vec2 two_sum(float a, float b)
{
float v,s,e;
s = a+b; // double s = a + b;
v = s-a; // double bb = s - a;
e = (a-(s-v))+(b-v); // err = (a - (s - bb)) + (b - bb);
return vec2(s,e);
}
vec2 split(float a)
{
float t, hi;
t = 8193. * a;
hi = t - (t-a);
return vec2(hi, a-hi);
}
vec3 three_sum(float a, float b, float c)
{
vec2 tmp;
vec3 res;// = vec3(0.);
float t1, t2, t3;
tmp = two_sum(a, b); // t1 = qd::two_sum(a, b, t2);
t1 = tmp.x;
t2 = tmp.y;
tmp = two_sum(c, t1); // a = qd::two_sum(c, t1, t3);
res.x = tmp.x;
t3 = tmp.y;
tmp = two_sum(t2, t3); // b = qd::two_sum(t2, t3, c);
res.y = tmp.x;
res.z = tmp.y;
return res;
}
//inline void three_sum2(double &a, double &b, double &c)
vec3 three_sum2(float a, float b, float c)
{
vec2 tmp;
vec3 res;// = vec3(0.);
float t1, t2, t3; // double t1, t2, t3;
tmp = two_sum(a, b); // t1 = qd::two_sum(a, b, t2);
t1 = tmp.x;
t2 = tmp.y;
tmp = two_sum(c, t1); // a = qd::two_sum(c, t1, t3);
res.x = tmp.x;
t3 = tmp.y;
res.y = t2 + t3; // b = t2 + t3;
return res;
}
vec2 two_prod(float a, float b)
{
float p, e;
vec2 va, vb;
p=a*b;
va = split(a);
vb = split(b);
e = ((va.x*vb.x-p) + va.x*vb.y + va.y*vb.x) + va.y*vb.y;
return vec2(p, e);
}
vec4 renorm(float c0, float c1, float c2, float c3, float c4)
{
float s0, s1, s2 = 0.0, s3 = 0.0;
vec2 tmp;
// if (QD_ISINF(c0)) return;
tmp = quick_2sum(c3,c4); // s0 = qd::quick_two_sum(c3, c4, c4);
s0 = tmp.x;
c4 = tmp.y;
tmp = quick_2sum(c2,s0); // s0 = qd::quick_two_sum(c2, s0, c3);
s0 = tmp.x;
c3 = tmp.y;
tmp = quick_2sum(c1,s0); // s0 = qd::quick_two_sum(c1, s0, c2);
s0 = tmp.x;
c2 = tmp.y;
tmp = quick_2sum(c0,s0); // c0 = qd::quick_two_sum(c0, s0, c1);
c0 = tmp.x;
c1 = tmp.y;
s0 = c0;
s1 = c1;
tmp = quick_2sum(c0,c1); // s0 = qd::quick_two_sum(c0, c1, s1);
s0 = tmp.x;
s1 = tmp.y;
if (s1 != 0.0) {
tmp = quick_2sum(s1,c2); // s1 = qd::quick_two_sum(s1, c2, s2);
s1 = tmp.x;
s2 = tmp.y;
if (s2 != 0.0) {
tmp = quick_2sum(s2,c3); // s2 = qd::quick_two_sum(s2, c3, s3);
s2 = tmp.x;
s3 = tmp.y;
if (s3 != 0.0)
s3 += c4;
else
s2 += c4;
} else {
tmp = quick_2sum(s1,c3); // s1 = qd::quick_two_sum(s1, c3, s2);
s1 = tmp.x;
s2 = tmp.y;
if (s2 != 0.0){
tmp = quick_2sum(s2,c4); // s2 = qd::quick_two_sum(s2, c4, s3);
s2 = tmp.x;
s3 = tmp.y;}
else{
tmp = quick_2sum(s1,c4); // s1 = qd::quick_two_sum(s1, c4, s2);
s1 = tmp.x;
s2 = tmp.y;}
}
} else {
tmp = quick_2sum(s0,c2); // s0 = qd::quick_two_sum(s0, c2, s1);
s0 = tmp.x;
s1 = tmp.y;
if (s1 != 0.0) {
tmp = quick_2sum(s1,c3); // s1 = qd::quick_two_sum(s1, c3, s2);
s1 = tmp.x;
s2 = tmp.y;
if (s2 != 0.0){
tmp = quick_2sum(s2,c4); // s2 = qd::quick_two_sum(s2, c4, s3);
s2 = tmp.x;
s3 = tmp.y;}
else{
tmp = quick_2sum(s1,c4); // s1 = qd::quick_two_sum(s1, c4, s2);
s1 = tmp.x;
s2 = tmp.y;}
} else {
tmp = quick_2sum(s0,c3); // s0 = qd::quick_two_sum(s0, c3, s1);
s0 = tmp.x;
s1 = tmp.y;
if (s1 != 0.0){
tmp = quick_2sum(s1,c4); // s1 = qd::quick_two_sum(s1, c4, s2);
s1 = tmp.x;
s2 = tmp.y;}
else{
tmp = quick_2sum(s0,c4); // s0 = qd::quick_two_sum(s0, c4, s1);
s0 = tmp.x;
s1 = tmp.y;}
}
}
return vec4(s0, s1, s2, s3);
}
vec4 renorm4(float c0, float c1, float c2, float c3)
{
float s0, s1, s2 = 0.0, s3 = 0.0;
vec2 tmp;
// if (QD_ISINF(c0)) return;
tmp = quick_2sum(c2,c3); // s0 = qd::quick_two_sum(c2, c3, c3);
s0 = tmp.x;
c3 = tmp.y;
tmp = quick_2sum(c1,s0); // s0 = qd::quick_two_sum(c1, s0, c2);
s0 = tmp.x;
c2 = tmp.y;
tmp = quick_2sum(c0,s0); // c0 = qd::quick_two_sum(c0, s0, c1);
c0 = tmp.x;
c1 = tmp.y;
s0 = c0;
s1 = c1;
if (s1 != 0.0) {
tmp = quick_2sum(s1,c2); // s1 = qd::quick_two_sum(s1, c2, s2);
s1 = tmp.x;
s2 = tmp.y;
if (s2 != 0.0){
tmp = quick_2sum(s2,c3); // s2 = qd::quick_two_sum(s2, c3, s3);
s2 = tmp.x;
s3 = tmp.y;}
else{
tmp = quick_2sum(s1,c3); // s1 = qd::quick_two_sum(s1, c3, s2);
s1 = tmp.x;
s2 = tmp.y;}
} else {
tmp = quick_2sum(s0,c2); // s0 = qd::quick_two_sum(s0, c2, s1);
s0 = tmp.x;
s1 = tmp.y;
if (s1 != 0.0){
tmp = quick_2sum(s1,c3); // s1 = qd::quick_two_sum(s1, c3, s2);
s1 = tmp.x;
s2 = tmp.y;}
else{
tmp = quick_2sum(s0,c3); // s0 = qd::quick_two_sum(s0, c3, s1);
s0 = tmp.x;
s1 = tmp.y;}
}
return vec4(s0, s1, s2, s3);
}
vec3 quick_three_accum(float a, float b, float c)
{
vec2 tmp;
float s;
bool za, zb;
tmp = two_sum(b, c); // s = qd::two_sum(b, c, b);
s = tmp.x;
b = tmp.y;
tmp = two_sum(a, s); // s = qd::two_sum(a, s, a);
s = tmp.x;
a = tmp.y;
za = (a != 0.0);
zb = (b != 0.0);
if (za && zb)
return vec3(a,b,s);
if (!zb) {
b = a;
a = s;
} else {
a = s;
}
return vec3(a,b,0.);
}
// inline qd_real qd_real::ieee_add(const qd_real &a, const qd_real &b)
vec4 qs_ieee_add(vec4 _a, vec4 _b)
{
vec2 tmp=vec2(0.);
vec3 tmp3=vec3(0.);
int i, j, k;
float s, t;
float u, v; // double-length accumulator
float x[4] = float[4](0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
float a[4], b[4];
a[0] = _a.x;
a[1] = _a.y;
a[2] = _a.z;
a[3] = _a.w;
b[0] = _b.x;
b[1] = _b.y;
b[2] = _b.z;
b[3] = _b.w;
i = j = k = 0;
if (abs(a[i]) > abs(b[j]))
u = a[i++];
else
u = b[j++];
if (abs(a[i]) > abs(b[j]))
v = a[i++];
else
v = b[j++];
tmp = quick_2sum(u,v); // u = qd::quick_two_sum(u, v, v);
u = tmp.x;
v = tmp.y;
while (k < 4) {
if (i >= 4 && j >= 4) {
x[k] = u;
if (k < 3)
x[++k] = v;
break;
}
if (i >= 4)
t = b[j++];
else if (j >= 4)
t = a[i++];
else if (abs(a[i]) > abs(b[j])) {
t = a[i++];
} else
t = b[j++];
tmp3 = quick_three_accum(u,v,t) ; // s = qd::quick_three_accum(u, v, t);
u = tmp3.x;
v = tmp3.y;
s = tmp3.z;
if (s != 0.0) {
x[k++] = s;
}
}
// add the rest.
for (k = i; k < 4; k++)
x[3] += a[k];
for (k = j; k < 4; k++)
x[3] += b[k];
// qd::renorm(x[0], x[1], x[2], x[3]);
// return qd_real(x[0], x[1], x[2], x[3]);
return renorm4(x[0], x[1], x[2], x[3]);
}
// inline qd_real qd_real::sloppy_add(const qd_real &a, const qd_real &b)
vec4 qs_sloppy_add(vec4 a, vec4 b)
{
float s0, s1, s2, s3;
float t0, t1, t2, t3;
float v0, v1, v2, v3;
float u0, u1, u2, u3;
float w0, w1, w2, w3;
vec2 tmp;
vec3 tmp3;
s0 = a.x + b.x; // s0 = a[0] + b[0];
s1 = a.y + b.y; // s1 = a[1] + b[1];
s2 = a.z + b.z; // s2 = a[2] + b[2];
s3 = a.w + b.w; // s3 = a[3] + b[3];
v0 = s0 - a.x; // v0 = s0 - a[0];
v1 = s1 - a.y; // v1 = s1 - a[1];
v2 = s2 - a.z; // v2 = s2 - a[2];
v3 = s3 - a.w; // v3 = s3 - a[3];
u0 = s0 - v0;
u1 = s1 - v1;
u2 = s2 - v2;
u3 = s3 - v3;
w0 = a.x - u0; // w0 = a[0] - u0;
w1 = a.y - u1; // w1 = a[1] - u1;
w2 = a.z - u2; // w2 = a[2] - u2;
w3 = a.w - u3; // w3 = a[3] - u3;
u0 = b.x - v0; // u0 = b[0] - v0;
u1 = b.y - v1; // u1 = b[1] - v1;
u2 = b.z - v2; // u2 = b[2] - v2;
u3 = b.w - v3; // u3 = b[3] - v3;
t0 = w0 + u0;
t1 = w1 + u1;
t2 = w2 + u2;
t3 = w3 + u3;
tmp = two_sum(s1, t0); // s1 = qd::two_sum(s1, t0, t0);
s1 = tmp.x;
t0 = tmp.y;
tmp3 = three_sum(s2, t0, t1); // qd::three_sum(s2, t0, t1);
s2 = tmp3.x;
t0 = tmp3.y;
t1 = tmp3.z;
tmp3 = three_sum2(s3, t0, t2); // qd::three_sum2(s3, t0, t2);
s3 = tmp3.x;
t0 = tmp3.y;
t2 = tmp3.z;
t0 = t0 + t1 + t3;
// qd::renorm(s0, s1, s2, s3, t0);
return renorm(s0, s1, s2, s3, t0); // return qd_real(s0, s1, s2, s3);
}
vec4 qs_add(vec4 _a, vec4 _b)
{
return qs_sloppy_add(_a, _b);
// return qs_ieee_add(_a, _b);
}
vec4 qs_mul(vec4 a, vec4 b)
{
float p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5;
float q0, q1, q2, q3, q4, q5;
float t0, t1;
float s0, s1, s2;
vec2 tmp;
vec3 tmp3;
tmp = two_prod(a.x, b.x); // p0 = qd::two_prod(a[0], b[0], q0);
p0 = tmp.x;
q0 = tmp.y;
tmp = two_prod(a.x, b.y); // p1 = qd::two_prod(a[0], b[1], q1);
p1 = tmp.x;
q1 = tmp.y;
tmp = two_prod(a.y, b.x); // p2 = qd::two_prod(a[1], b[0], q2);
p2 = tmp.x;
q2 = tmp.y;
tmp = two_prod(a.x, b.z); // p3 = qd::two_prod(a[0], b[2], q3);
p3 = tmp.x;
q3 = tmp.y;
tmp = two_prod(a.y, b.y); // p4 = qd::two_prod(a[1], b[1], q4);
p4 = tmp.x;
q4 = tmp.y;
tmp = two_prod(a.z, b.x); // p5 = qd::two_prod(a[2], b[0], q5);
p5 = tmp.x;
q5 = tmp.y;
/* Start Accumulation */
tmp3 = three_sum(p1, p2, q0); // qd::three_sum(p1, p2, q0);
p1 = tmp3.x;
p2 = tmp3.y;
q0 = tmp3.z;
/* Six-Three Sum of p2, q1, q2, p3, p4, p5. */
tmp3 = three_sum(p2, q1, q2); // qd::three_sum(p2, q1, q2);
p2 = tmp3.x;
q1 = tmp3.y;
q2 = tmp3.z;
tmp3 = three_sum(p3, p4, p5); // qd::three_sum(p3, p4, p5);
p3 = tmp3.x;
p4 = tmp3.y;
p5 = tmp3.z;
/* compute (s0, s1, s2) = (p2, q1, q2) + (p3, p4, p5). */
tmp = two_sum(p2, p3); // s0 = qd::two_sum(p2, p3, t0);
s0 = tmp.x;
t0 = tmp.y;
tmp = two_sum(q1, p4); // s1 = qd::two_sum(q1, p4, t1);
s1 = tmp.x;
t1 = tmp.y;
s2 = q2 + p5;
tmp = two_sum(s1, t0); // s1 = qd::two_sum(s1, t0, t0);
s1 = tmp.x;
t0 = tmp.y;
s2 += (t0 + t1);
/* O(eps^3) order terms */
s1 += a.x*b.w + a.y*b.z + a.z*b.y + a.w*b.x + q0 + q3 + q4 + q5;
return renorm(p0, p1, s0, s1, s2); // qd::renorm(p0, p1, s0, s1, s2);
}
float ds_compare(vec2 dsa, vec2 dsb)
{
if (dsa.x < dsb.x) return -1.;
else if (dsa.x == dsb.x)
{
if (dsa.y < dsb.y) return -1.;
else if (dsa.y == dsb.y) return 0.;
else return 1.;
}
else return 1.;
}
float qs_compare(vec4 qsa, vec4 qsb)
{
if(ds_compare(qsa.xy, qsb.xy)<0.) return -1.; // if (dsa.x < dsb.x) return -1.;
else if (ds_compare(qsa.xy, qsb.xy) == 0.) // else if (dsa.x == dsb.x)
{
if(ds_compare(qsa.zw, qsb.zw)<0.) return -1.; // if (dsa.y < dsb.y) return -1.;
else if (ds_compare(qsa.zw, qsb.zw) == 0.) return 0.;// else if (dsa.y == dsb.y) return 0.;
else return 1.;
}
else return 1.;
}
float qs_mandel(void)
{
vec4 qs_tx = vec4(gl_TexCoord[0].x, vec3(0.)); // get position of current pixel
vec4 qs_ty = vec4(gl_TexCoord[0].y, vec3(0.));
// initialize complex variable with respect to current position, zoom, ...
vec4 cx = qs_add(qs_add(vec4(qs_cx,0.,0.),qs_mul(qs_tx,vec4(qs_z,0.,0.))),vec4(qs_w,0.,0.));
vec4 cy = qs_add(qs_add(vec4(qs_cy,0.,0.),qs_mul(qs_ty,vec4(qs_z,0.,0.))),vec4(qs_h,0.,0.));
vec4 tmp;
vec4 zx = cx;
vec4 zy = cy;
vec4 two = vec4(2.0, vec3(0.));
vec4 e_radius = vec4(radius*radius, vec3(0.)); // no sqrt available so compare with radius^2 = 2^2 = 2*2 = 4
for(int n=0; n<iterations; n++)
{
tmp = zx;
zx = qs_add(qs_add(qs_mul(zx, zx), -qs_mul(zy, zy)), cx);
zy = qs_add(qs_mul(qs_mul(zy, tmp), two), cy);
if( qs_compare(qs_add(qs_mul(zx, zx), qs_mul(zy, zy)), e_radius)>0.)
{
return(float(n) + 1. - log(log(length(vec2(zx.x, zy.x))))/log(2.)); // http://linas.org/art-gallery/escape/escape.html
}
}
return 0.;
}
void main()
{
float n = qs_mandel();
gl_FragColor = vec4((-cos(0.025*n)+1.0)/2.0,
(-cos(0.08*n)+1.0)/2.0,
(-cos(0.12*n)+1.0)/2.0,
1.0);
}
Please note that there are two methods in the qs_add-function to add two quad-singles: “sloppy_add”, which is faster and less accurate and “ieee_add” (nice and slow). You can use either of them.
Result
It actually works! New worlds of our mandelbrot lay ahead. Undiscovered features can be made visible with just a blink of our GPU eye.
Performance
Quad-Single works fine but is really slooooooooow… See for yourself:
CPU: Intel i5-2400 @ 3.1 GHz GPU: ATI HD4870
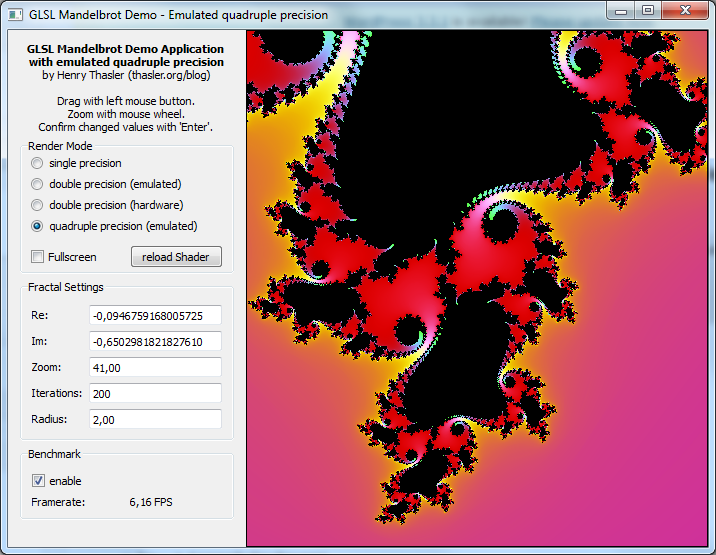
Compared with emulated double precision (51 FPS) and hardware accelerated double precision (154 FPS) the emulated quad-precision (6 FPS) is taking it’s time.
Limitations
As you may have noticed if you actually tried this demo, zooming and scrolling beyond zoom levels of 48 is a bit inaccurate. This is due to the limited precision of the variables that the main (Qt) program hands over to the shader. It uses double precision (more precisely: emulated double) and is limited to a minimal step width that is well above the quad single precision of the shader. This is an issue I’m going to solve in another post (hopefully…).
Conclusion
Quadruple precision is - in terms of computational resources - very expensive to implement. It is suitable for real-time applications if you stick with simple calculations.
Eric Bainville has written some code for fp128 (128-bit fixed point numbers). Maybe I can try this with GLSL in the future and see how it performs.
The reduced computing precision (only long doubles are generally available in Qt) on the Qt side is currently limiting the possibilities of the shader performance. An equal or higher precision as in the shader is required to explore the full depth of the emulated quadruple precision in GLSL. Maybe the quad-single concept can be extended to quad-double.